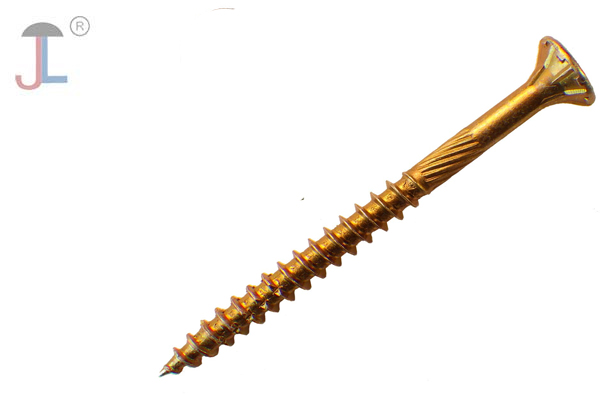
Phosphate coated screws do offer resistance to rust and corrosion, but they are not completely rust-proof. The phosphate coating acts as a protective barrier that helps prevent moisture and corrosive substances from reaching the underlying metal. Compared to uncoated screws, phosphate-coated screws have significantly higher resistance to rust.
However, the coating is porous and can be damaged during installation or use. If the phosphate coating is scratched or exposed to harsh environments, rust can eventually develop. For optimal rust resistance, proper precautions should be taken such as storing screws in dry conditions, avoiding over-tightening which can damage the coating, keeping the screws clean, and considering additional rust inhibitors if used in corrosive environments.

There are different types of phosphate coatings, such as gray phosphate (zinc phosphate) and black phosphate (manganese phosphate). Gray phosphate screws tend to offer slightly better corrosion resistance than black phosphate screws. Still, both coatings are intended primarily for indoor or less harsh applications, as their corrosion resistance may not be sufficient for prolonged outdoor exposure.
In summary, phosphate coated screws are rust resistant to a good degree but not completely rust-proof. Proper handling and environmental considerations are important to maintain their corrosion resistance over time.