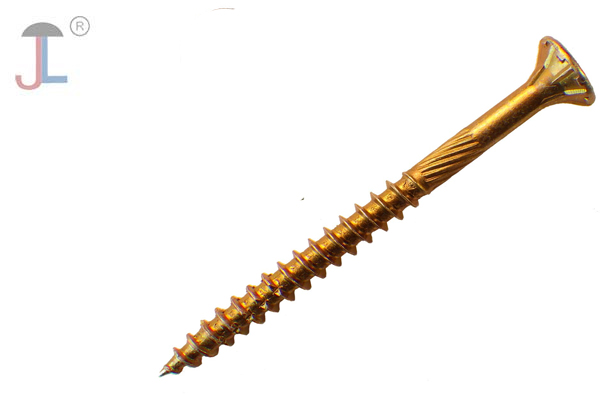
Galvanized and phosphate-coated screws offer distinct advantages for different applications. Galvanized screws, typically coated with zinc, provide superior, long-lasting corrosion resistance, especially in outdoor environments. Phosphate coatings, on the other hand, are primarily used to enhance lubrication, paint adhesion, and wear resistance, making them suitable for interior applications or as a base for further coatings.
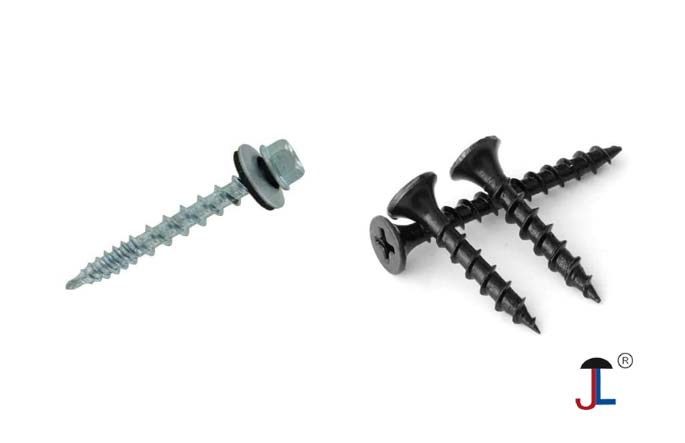

Galvanized Screws:
- Corrosion Protection: Galvanization involves coating steel with zinc, which acts as a sacrificial layer, corroding before the underlying steel and thus preventing rust and corrosion.
- Outdoor Use: Due to their superior corrosion resistance, galvanized screws are ideal for outdoor applications, construction, and marine environments.
- Appearance: Galvanized screws typically have a dull silver appearance.
- Durability: Galvanized coatings, especially hot-dip galvanization, can provide very durable protection against rust and corrosion.
Phosphate Coated Screws:
- Lubrication and Paint Adhesion: Phosphate coatings create a porous layer that can retain oil or other lubricants, reducing friction during installation and enhancing paint adhesion.
- Interior Use: Phosphate coatings are often used on screws for interior applications, where corrosion resistance is not the primary concern.
- Appearance: Phosphate coatings typically have a dull gray or black appearance.
- Base for Further Coatings: Phosphate coatings can serve as a base for other coatings, such as paint, enhancing their adhesion and performance.
- Galling Prevention: Phosphate coatings can also help prevent galling (a type of wear) on fasteners, especially those subjected to high friction.
In Summary
If you need long-lasting corrosion protection for outdoor or marine applications, galvanized screws are the better choice. If you need a coating to enhance lubrication, paint adhesion, or wear resistance, especially for interior applications, phosphate-coated screws are more suitable.