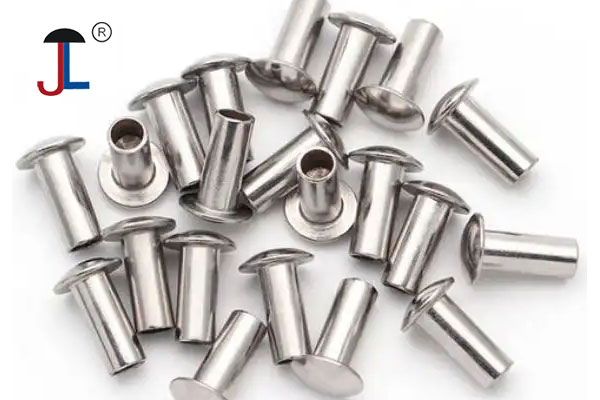
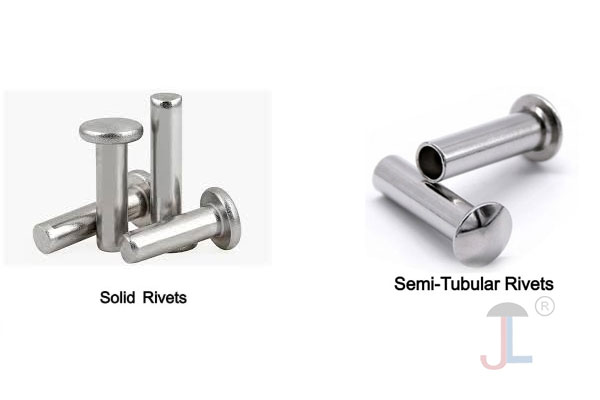
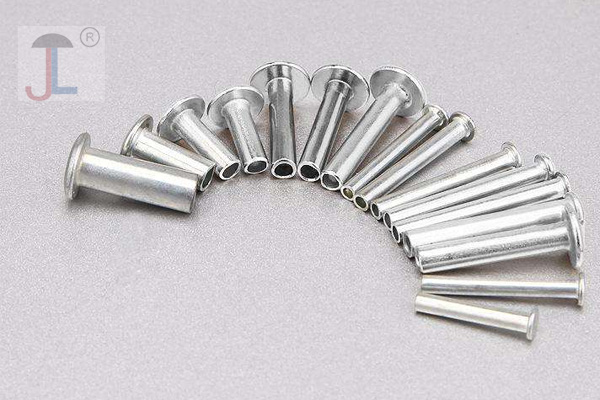
Hollow Rivet
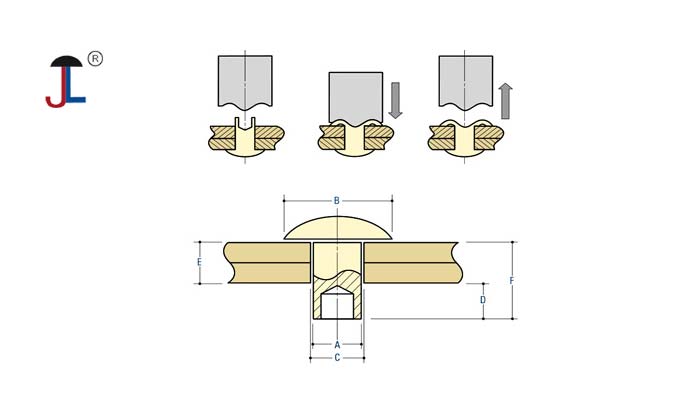
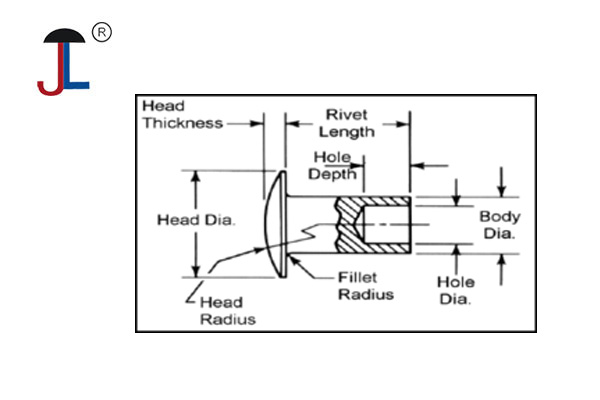
- A hollow rivet, also known as a tubular rivet, is a type of rivet that has a hollow core running through its shaft. It is essentially a solid rivet with a cylindrical hole through it, which reduces the force needed for installation while maintaining joint strength.
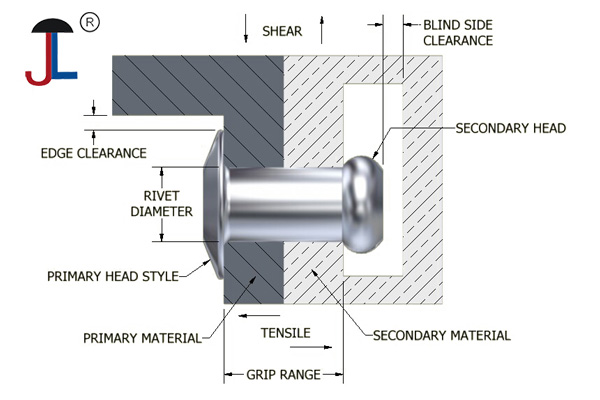
- Hollow rivets are used to permanently fasten materials together by deforming the tail end after insertion, creating a strong mechanical bond.
- They are typically made from metals like aluminum, steel, brass, copper, or stainless steel and are used in applications where moderate strength and lightweight fastening are required.
- Hollow rivets are often used to join softer materials or to fasten components where some vibration damping is beneficial.
Eyelet
- An eyelet is a small metal tube with flared ends that creates a reinforced hole in a material. Unlike rivets, eyelets are designed to provide a passage or opening through which cords, laces, wires, or chains can be threaded.
- The key feature of an eyelet is that it remains hollow and open all the way through after installation, allowing something to pass through the hole. In contrast, at least one end of a rivet is always solid, preventing passage through it.
- Eyelets are commonly used in textiles, leather goods, tarps, shoes, and other items where a durable, reinforced hole is needed for lacing or fastening.
- Eyelets are installed by flaring the ends to clamp the material securely without permanently joining two pieces together like rivets do.
| Feature | Hollow Rivet | Eyelet |
|---|---|---|
| Structure | Hollow shaft with one solid end | Hollow tube open through both ends |
| Purpose | Permanent fastening of materials | Creating a reinforced hole for threading |
| Installation | Deformed tail to form a mechanical joint | Flared ends to clamp material |
| Function | Joins materials together firmly | Allows passage of cord, lace, wire |
| Common Uses | Mechanical assembly, electronics, leather goods | Shoes, tarps, textiles, leather goods |
| Material | Metals like aluminum, steel, brass | Metals, often brass or steel |